This write-up is an insight into the persistence layer of Twitter. It covers topics such as what database does it use? Is it SQL, NoSQL, or a polyglot persistent system? How does it store hundreds of millions of tweets sent every single day? and more.
I’ll begin with the gist first, list out the databases and then will talk about each one of them in detail.
So, without further ado. Let’s jump right in.
Distributed Systems
For a complete list of similar articles on distributed systems and real-world architectures, here you go
1. What Database Does Twitter Use?
Hadoop for social graph analysis, recommendations, trends, API analytics, user engagement prediction, ad targeting, ad analytics, tweet impressions processing, taking MySQL backups, Manhattan backups & storing front-end scribe logs.
MySQL & Manhattan: the primary data stores for storing user data.
Memcache, Redis for caching
FlockDB for storing social graph
MetricsDB for storing platform data metrics
Blobstore for storing images, videos & large binary objects.
Now let’s talk about all the data stores individually.
2. Hadoop
Twitter runs one of the biggest Hadoop clusters in the world. Hadoop was originally used at Twitter to take MySQL backups & then over time, its use cases on the platform grew to quite an extent.
Today, It is used to store data to run analytics on the actions the users perform on the platform. Social graph analysis, recommendations, trends, API analytics, user engagement prediction, Ad targeting, ad analytics, tweet impressions processing, taking MySQL backups, Manhattan backups & storing front end scribe logs.
The Hadoop file system stores over 500 petabytes of data running over tens of thousands of instances. The entire cluster is managed using the Hadoop Federation feature running hundreds of thousands of daily Hadoop jobs and tens of millions of daily Hadoop tasks.
150K+ services & 130M containers are running on any regular day.
To scale the services Hadoop uses different namespaces. The nodes with namespaces, also known as Namenodes, run independently & have no dependence on each other.
There are nodes called data nodes which are used for data storage by the Namenodes. These data nodes are registered with the Namenodes in the cluster.
To manage the namespaces, View file system is used, which is useful for managing clusters having multiple Namenodes.
Every cluster has more than 3500 Namenodes.
3. Manhattan: A NoSQL Eventually Consistent Data Store
Manhattan is a real-time multi-tenant scalable distributed database used at Twitter to serve millions of queries per second with really low latency being highly available.
It stores user tweets, direct messages, account details, etc. On any given day, Manhattan clusters handle tens of millions of queries per second.
Why Manhattan?
The real-time nature of the platform requires very low latency which the existing open-source solutions couldn’t offer.
A lot of resources were spent on managing & trying to stoke up the performance of the existing storage systems. This prognosis wasn’t good, the existing persistence system wouldn’t have worked in the long run. This led to the development of Manhattan.
The requirements to build Manhattan were simple like having a reliable datastore with predictable performance, availability, extensibility, easy operability working with hundreds of thousands of nodes & scalability.
Manhattan is separated into four layers interfaces, storage services, storage engines and the core with an eventual consistency model.
High availability is preferred over strong consistency. Replication is extensively used to keep Manhattan highly available.
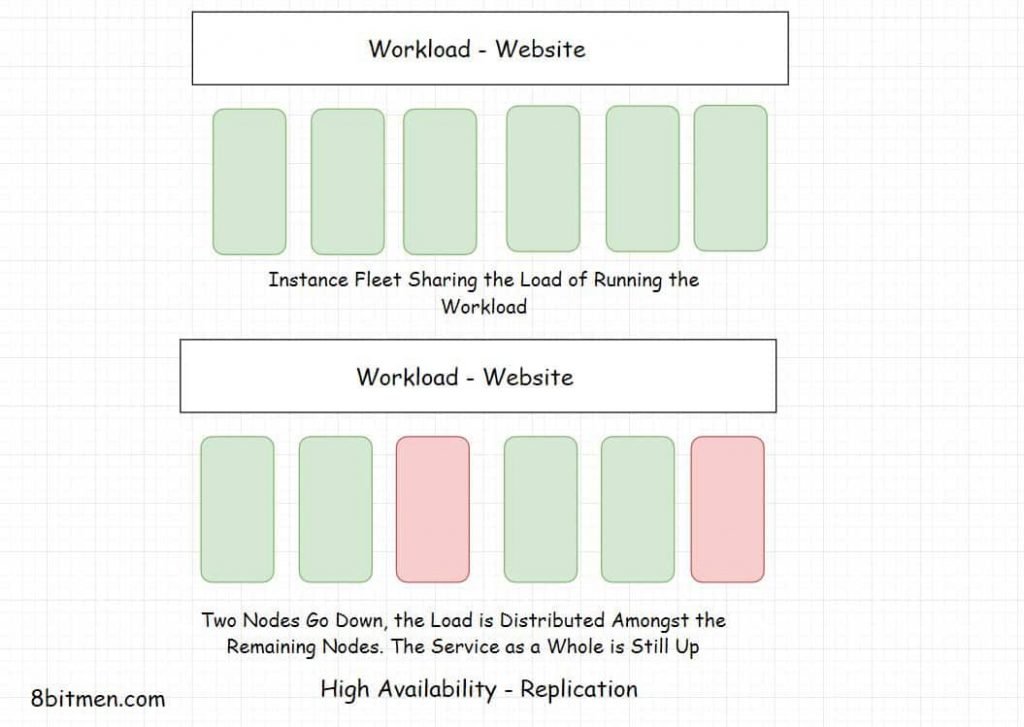
The storage engine of Manhattan was designed in-house with a pluggability feature to enable plugging of any external storage engines if & when required in the future.
4. BlobStore – Image Video & Large Object Storage System
Blobstore is Twitter’s scalable storage system to store user images, videos & other large binary objects. It has enabled Twitter to cut down costs associated with storing user uploaded images with Tweets.
It is a highly performant system capable of serving images in low tens of milliseconds while having a throughput of hundreds of thousands of requests per second.
When the image is uploaded to the Blobstore, it synchronizes the image across all of Twitter’s data centers with the help of an asynchronous queue server.
5. Caching at Twitter With Memcache & Redis
With caching implemented Twitter delivers approx. 120 GB of data per second to the clients.
Twitter built Twemcache, a custom version of Memcache suited for large-scale production deployment.
The platform has hundreds of cache instances having over 20TB of data in-memory from over 30 services. Comprehensively, the caching layer serves over 2 trillion queries on any regular day.
Caching at Twitter has two primary use cases:
The first is the obvious one, having in-memory data to avoid database hits. The second, it is used as a memory buffer to store items that are expensive to compute over and over.
Twemproxy, a lightweight proxy for Memcache & Redis protocol, enables the caching layer to scale horizontally minimizing the connections to the backend caching servers.
Twitter internally runs many caching services & one of them is powered by Redis. Redis clusters cache direct user messages, ad spends, impressions & engagement.
There is another caching service, Haplo which acts as a primary cache for the Twitter Timeline. It’s backed by Redis.
6. Relational Databases – MySQL, PostgreSQL, Vertica
MySQL
Twitter started with MySQL as the primary data store, from a single instance the persistence layer grew to a large number of clusters.
Twitter has had one of the biggest deployments of MySQL right from its inception. It has MySQL clusters with thousands of nodes serving millions of queries per second.
MySQL has primarily two use cases:
1. Acting as the storage node for the distributed data store within Twitter’s sharding framework. MySQL storage nodes provide reliability & performance in the overall distributed store.
2. Powers services such as ads, authentication, Twitter trends & many internal services.
The engineering team at Twitter has also built a scalable MySQL database service framework called Mysos.
It is based on Apache Mesos. Mesos enables Mysos to schedule, monitor & communicate with MySQL instances in the cluster. MySQL instances were sharded with the help of a framework for creating distributed datastores called Gizzard.
Besides MySQL, other SQL-based data stores like PostgreSQL & Vertica are also used to store ad campaigns, sales & internal tooling data.
Cassandra is also used with MySQL as a data storage solution but it lacked the auto-increment feature which MySQL had. It did store metrics for a while & was later deprecated after Twitter started using Manhattan.
7. Metrics DB – Time Series Database For Storing Metrics
Metrics DB is used at Twitter to store the metrics. The metric ingestion rate is more than 5 billion metrics per minute with 25K query requests per minute.
Originally, Manhattan was used as the metric storage database but Twitter faced scalability issues along with not having support for additional minute metric tags.
This led to the development of Metrics DB in-house using the compression algorithm of Facebook’s in-memory Time-series Database Gorilla.
Metrics DB provides multi-zone support, partitioning of metrics & compression efficiency over other data stores used at Twitter. Using Gorilla’s compression algorithm, Twitter reduced its space usage by 95%.
8. Social Graph Storage with FlockDB
FlockDB is a distributed graph datastore built for fast graph traversals, storing adjacency lists, supporting a high rate of add, remove, and update operations, paginating through millions of entries, horizontally scaling, and running graph walking queries.
Twitter used it to store social graph with information such as who follows whom & such.
Recommended read: Twitter’s Migration to Google Cloud
Well, Folks! This is pretty much it. If you liked the write-up, consider sharing it with your network for more reach.
I am Shivang. You can read more about me here.
Check out the Zero to Mastering Software Architecture learning path, a series of three courses I have written intending to educate you, step by step, on the domain of software architecture and distributed system design. The learning path takes you right from having no knowledge in it to making you a pro in designing large-scale distributed systems like YouTube, Netflix, Hotstar, and more.
Shivang
Related posts
Zero to Mastering Software Architecture Learning Path - Starting from Zero to Designing Web-Scale Distributed Applications Like a Pro. Check it out.
Master system design for your interviews. Check out this blog post written by me.
Zero to Mastering Software Architecture is a learning path authored by me comprising a series of three courses for software developers, aspiring architects, product managers/owners, engineering managers, IT consultants and anyone looking to get a firm grasp on software architecture, application deployment infrastructure and distributed systems design starting right from zero. Check it out.
Recent Posts
- System Design Case Study #5: In-Memory Storage & In-Memory Databases – Storing Application Data In-Memory To Achieve Sub-Second Response Latency
- System Design Case Study #4: How WalkMe Engineering Scaled their Stateful Service Leveraging Pub-Sub Mechanism
- Why Stack Overflow Picked Svelte for their Overflow AI Feature And the Website UI
- A Discussion on Stateless & Stateful Services (Managing User State on the Backend)
- System Design Case Study #3: How Discord Scaled Their Member Update Feature Benchmarking Different Data Structures
CodeCrafters lets you build tools like Redis, Docker, Git and more from the bare bones. With their hands-on courses, you not only gain an in-depth understanding of distributed systems and advanced system design concepts but can also compare your project with the community and then finally navigate the official source code to see how it’s done.
Get 40% off with this link. (Affiliate)


Follow Me On Social Media